Table of Contents Link to heading
Why control statement Link to heading
Control statements allow actions to happen depending on a condition.
- The action may involve setting a value.
- The action may involve running a different query.
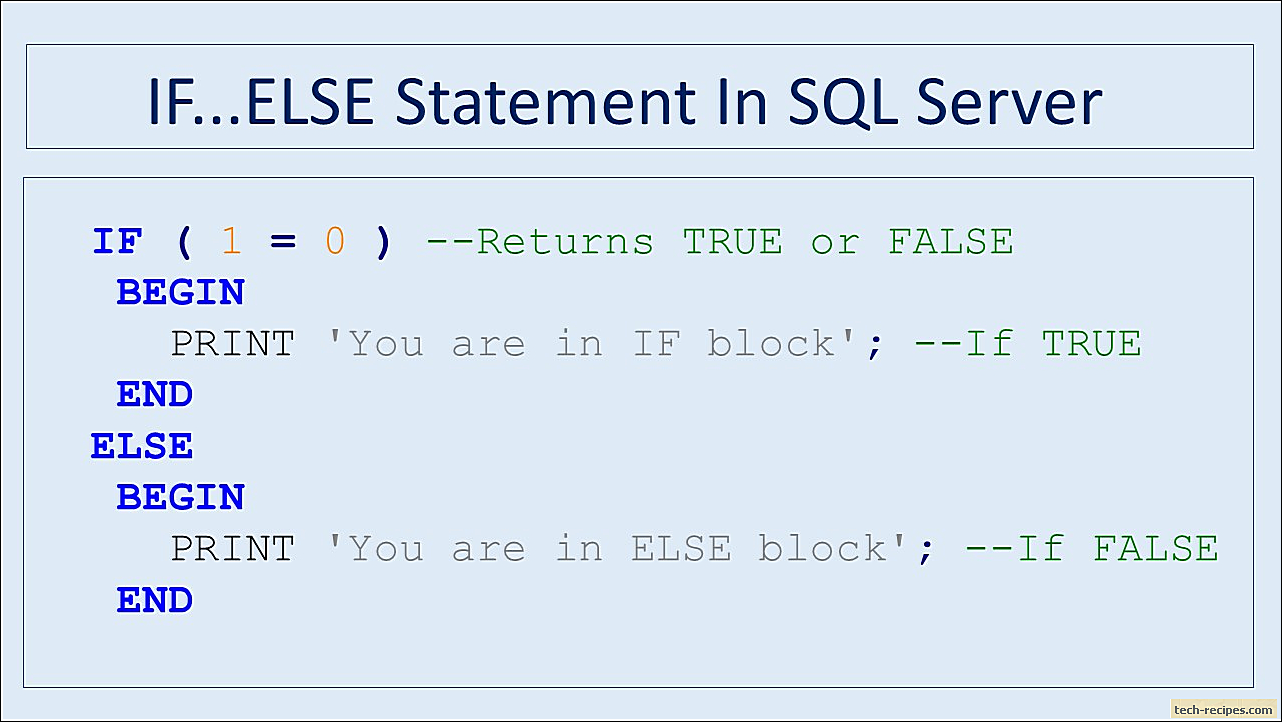
IF - ELSE statements
Link to heading
Syntax Link to heading
IF boolean_expression
{ sql_statement | statement_block }
[ ELSE
{ sql_statement | statement_block } ]
Arguments Link to heading
- boolean_expression
- Is an expression that returns TRUE or FALSE. If the Boolean expression contains a SELECT statement, the SELECT statement must be enclosed in parentheses.
- { sql_statement | statement_block }
- Is any Transact-SQL statement or statement grouping as defined by using a statement block. Unless a statement block is used, the IF or ELSE condition can affect the performance of only one Transact-SQL statement.
To define a statement block, use the control-of-flow keywords BEGIN and END.
Example Link to heading
IF DATENAME (dw, 2002-07-03) IN (N'Saturday', N'Sunday')
SELECT 'Weekend' AS result;
ELSE
SELECT 'Weekday' AS result;
Result:
| result |
|---|
| Weekday |
CASE statement
Link to heading
This statement is akin to IF…ELSE but can be used within a query to change a particular value.
Syntax Link to heading
CASE input_expression
WHEN when_expression THEN result_expression [ ...n ]
[ ELSE else_result_expression ]
END
Arguments Link to heading
- input_expression
- The expression evaluated when the simple CASE format is used. input_expression is any valid expression.
- WHEN when_expression
- A simple expression to which input_expression is compared when the simple CASE format is used. when_expression is any valid expression. The data types of input_expression and each when_expression must be the same or must be an implicit conversion.
- THEN result_expression
- The expression returned when input_expression equals when_expression evaluates to TRUE, or Boolean_expression evaluates to TRUE. result expression is any valid expression.
- ELSE else_result_expression
- The expression returned if no comparison operation evaluates to TRUE. If this argument is omitted and no comparison operation evaluates to TRUE, CASE returns NULL. else_result_expression is any valid expression. The data types of else_result_expression and any result_expression must be the same or must be an implicit conversion.
- WHEN Boolean_expression
- The Boolean expression evaluated when using the searched CASE format. Boolean_expression is any valid Boolean expression.
Example Link to heading
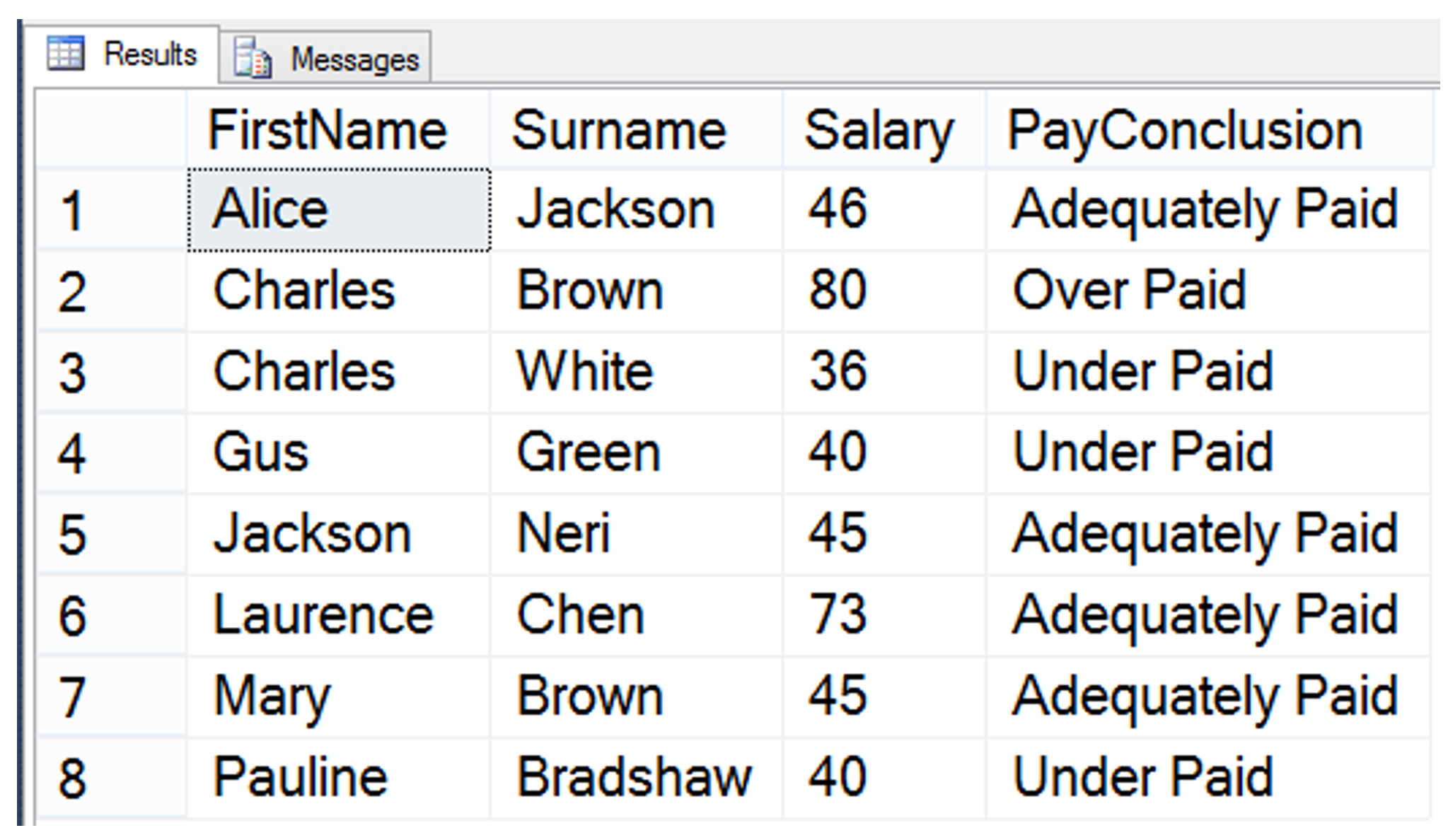
SELECT
FirstName,
Surname,
Salary,
(
CASE
WHEN (E.Salary > 75) THEN 'Over Paid'
WHEN (E.Salary <= 40) THEN 'Under Paid'
ELSE 'Adequately Paid'
END
) AS PayConclusion
FROM Employee AS E
- The CASE statement returns a single column called “PayConclusion” with value that depends on the employee salary.
Sample result: