Table of Contents Link to heading
- General Terminology
- Relations
- Attributes
- Types of Attributes
- Domains
- Table Schemas
- Tuples
- Put It All Together
General Terminology Link to heading
| Relational Name | Common Name | Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| relation | table | - |
| attribute | column | field |
| tuple | row | record |
Within a table, every column name must be UNIQUE.
Within a Table every row must be UNIQUE (no duplicate data!).
Every Row must have a unique Primary Key that can identify that data row only!
Relations Link to heading
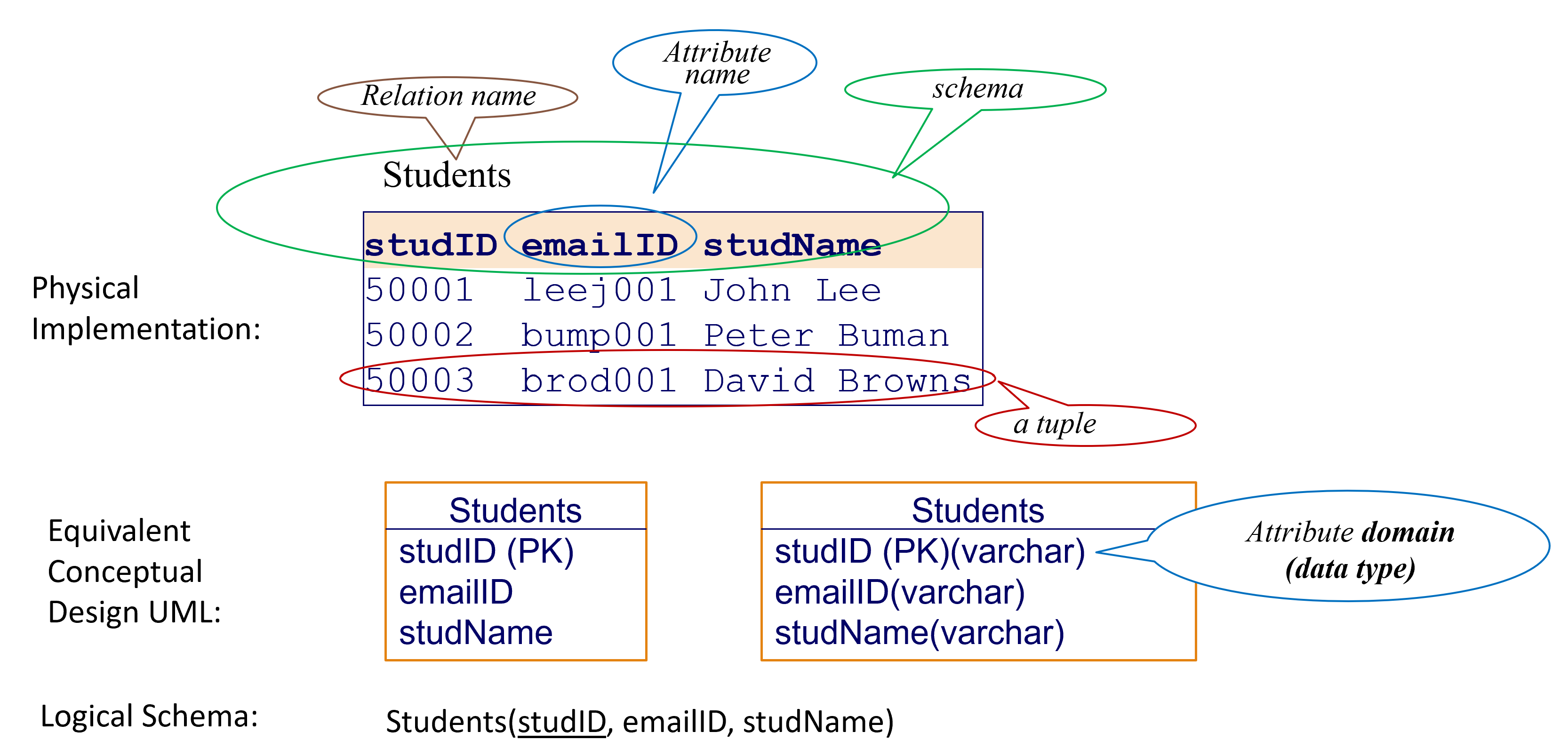
A RELATION defines a real world or conceptual object we collect information about.
When a relation is implemented in a Database Management System (DBMS), it is often called a table.
A relational database (model) consists of a series of relations with distinct names.
- It is a convention to name relations using the PascalCase.
For example, a School relation stores lecturerInfo, studentID, courses.
Attributes Link to heading
An ATTRIBUTE is a property that describes a relation.
Each attribute must have a unique name in a given relational table.
- It is a convention to name attributes using the camelCase.
For example, the School table (relation) has columns (attributes) for collecting the Lecturer’s information, Student ID, and Courses.
Every attribute has a domain.
Types of Attributes Link to heading
There are five types of attribute:
- Simple attributes are atomic values which cannot be divided further.
- They provide a single piece of useful information and not consist of subparts or multiple values or repeating information.
- E.g. A person’s phone number is an atomic value of 10 digits.
- Composite attributes are made of more than one simple attribute.
- E.g. A person’s complete name may have firstName and lastName attributes.
- Derived attributes are those whose values are calculated from the values of other attributes.
| PurchaseOrder |
|---|
| quantity |
| price |
| /total |
- total = quantity * price
- Thus, total is a Derived Attribute.
- Structured attributes are those composed of more than one attribute.
| Employee |
|---|
| name |
| salutation |
| firstName |
| lastName |
| address: |
| addressLine1 |
| addressLine2 |
- The name attribute consists of salutation + firstName + lastName.
- Thus name is a Structured Attribute.
- Single-valued attributes are those which simply contain a single value.
- E.g. taxFileNumber, socialSecurityNumber, etc.
- Multivalued attributes are those which contain more than one values.
- E.g. A person can have more than one phoneNumber, emailAddress, etc.
- It violates basic relational theory (single-valued attributes).
- To resolve a multivalued attribute, place it in a separate table and associate it with the original table.
For example:

Domains Link to heading
A Domain dictates (determines) the data type and the range of acceptable values of an attribute.
- A domain of possible values must be associated with every attribute (e.g., integer types, character types, date/time types).
Declaring an attribute to be of a particular domain acts as a constraint on the values that it can take. Domain constraints are the most elementary form of integrity constraint. They are tested easily by the system whenever a new data item is entered into the database.
Common Database data type include:
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| char(n) | Stores a fixed-length n-character string (text) |
| varchar(n) | Variable length character string (text) of maximum size n characters |
| int | An integer number (whole number) |
| decimal(m, n) | A decimal number of m total digits and n decimal places |
| date | A date value (day/month/year) – if using British standard |
| datetime | A date time value (day/month/year hr:min:sec AM/PM) |
| bit | A Boolean value (‘True’ and ‘False’ or 1 and 0) |
For example:
| Attribute Name | Domain |
|---|---|
| studentName | varchar(100) |
| favColour | varchar(10) {red, green, blue} |
Table Schemas Link to heading
A TABLE SCHEMA is the overall design of a relational table in a relational database.
Programming analogy: a database schema corresponds to the variable declarations (along with associated type definitions) in a program.
Format: RelationName(attributeNames)
Example: Customer(customerID, firstName, familyName, address, age)
Tuples Link to heading
A TUPLE is an instance of a relation or entity and contains the actual raw data.
To simplify, a Tuple is a row of data.
A relation consists of one or more unordered tuples.
Within a relation, every tuple has a fixed number of values, hence the name ’tuple’.
Put It All Together Link to heading
